Atomic Force Microscopy – AFM
With the technology improvement, beyond optical microscopes, there are strongests microscopes developed, like the SPM – Scanning Probe Microscope, that is divided in two classes: the STM – Scanning Tunneling Microscope and the AFM (Atomic Force Microscope) [1]. The images obtained by microscopy of AFM/STM are very important tools for the nanoscience and nanotechnology study. The LOOSA has an AFM of the company Nanosurf, model EasyScan 2 FlexAFM (image below) that allows to study the morphology of different surfaces like: polymeric, liquid crystals, metals, semiconductors, among others. Across investigate the morphologic surface characteristic of one sample, it can be explored the tribological properties, like the roughness, hardness, rigidity, elasticity, friction, among others.
[1] Binning, G., Quate, C.F.,Gerber, C. Atomic Force microscopy. Physical Review Letters, 1986, Vol. 56, 9, 930-933.
|
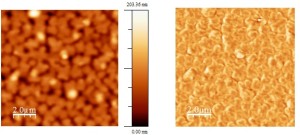
Liquid Crystal film: morphological image (left) and contrast of phase (right) |
|
|
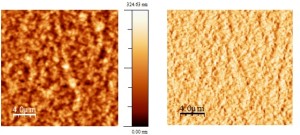
Film of P3HT:PCBM (60:40): morphological image (left) and contrast of phase (right) |
|
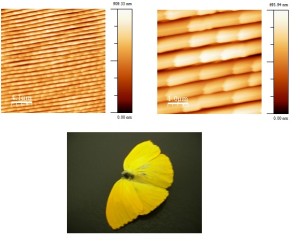
Morphological image obtained by AFM from the yellow butterfly wing’s surface. |